Rainbows have fascinated humanity for centuries, and understanding the sequence of rainbow colors is key to appreciating their beauty. From red to violet, the colors of a rainbow follow a specific order that has intrigued scientists and artists alike. This article delves into the science behind the sequence of rainbow colors, their cultural significance, and much more.
Rainbows are not just a natural phenomenon but also a symbol of hope, diversity, and beauty in many cultures. The sequence of colors in a rainbow is a result of the way light interacts with water droplets in the atmosphere. This article will explore the physics behind this mesmerizing phenomenon, offering insights that are both educational and captivating.
Whether you're a science enthusiast, a teacher looking for resources, or simply someone who appreciates the wonders of nature, this guide will provide you with all the information you need about the sequence of rainbow colors. Let's dive in!
Read also:Is Emily Compagno Married Exploring Her Personal Life And Career
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Rainbow Colors
- The Science Behind the Sequence
- Understanding the Order of Colors
- Physics of Light Refraction
- Historical Perspective of Rainbows
- Cultural Significance of Rainbows
- Double Rainbows and Their Colors
- Variations in Rainbow Colors
- Myths and Legends About Rainbows
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to Rainbow Colors
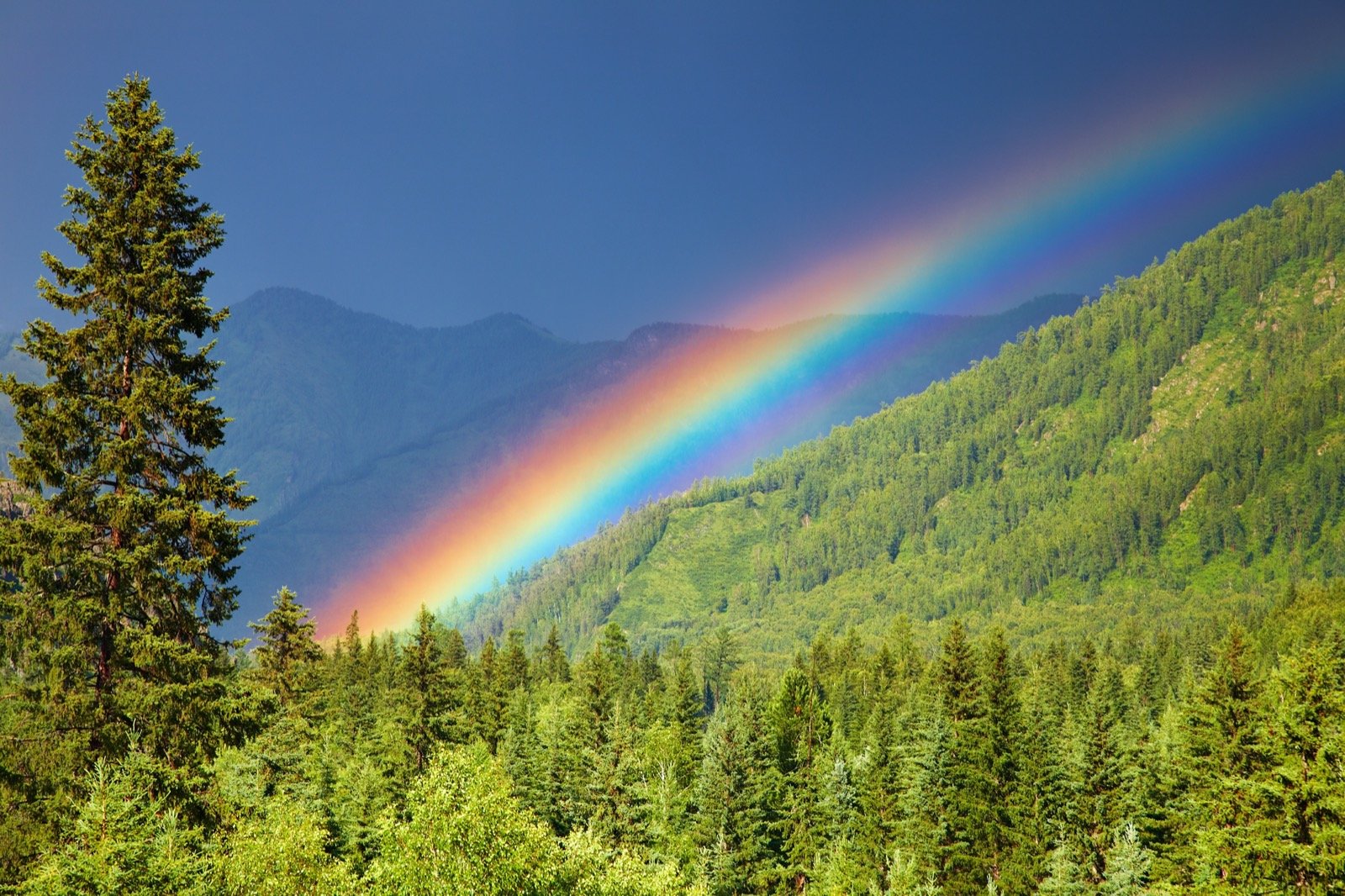
The sequence of rainbow colors is one of the most fascinating aspects of this natural phenomenon. When sunlight passes through water droplets in the atmosphere, it creates a spectrum of colors that appear in a specific order. The colors of a rainbow are always red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet, commonly remembered by the acronym "ROYGBIV."
Why Study Rainbow Colors?
Understanding the sequence of rainbow colors provides insight into the physics of light and how it interacts with the environment. It also highlights the beauty and complexity of natural phenomena. For educators, this topic serves as an engaging way to introduce students to the principles of optics and meteorology.
The Science Behind the Sequence
The sequence of rainbow colors is a result of the refraction, reflection, and dispersion of light within water droplets. When sunlight enters a droplet, it slows down and bends due to the change in medium. This bending causes the light to split into its constituent colors, each bending at a slightly different angle.
How Does Refraction Work?
- Light travels faster in air than in water.
- When light enters a water droplet, it slows down and bends.
- Each color bends at a different angle, creating the spectrum of colors.
Understanding the Order of Colors
The sequence of rainbow colors follows a specific order: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. This order is determined by the wavelength of each color, with red having the longest wavelength and violet the shortest.
Why Is the Order Always the Same?
The order of colors in a rainbow is consistent because it depends on the physical properties of light. Longer wavelengths, such as red, bend less than shorter wavelengths, such as violet, resulting in the familiar sequence.
Physics of Light Refraction
The physics of light refraction plays a crucial role in the formation of rainbows. When light enters a water droplet, it undergoes both refraction and reflection. The angle at which the light exits the droplet determines the position of each color in the rainbow.
Read also:Mike Lindell Net Worth 2025 A Comprehensive Analysis Of His Financial Journey
Key Principles of Refraction
- Snell's Law explains the bending of light as it passes through different mediums.
- Each color has a unique angle of refraction based on its wavelength.
- The combination of refraction and reflection creates the colorful arc we see in the sky.
Historical Perspective of Rainbows
Rainbows have been observed and studied for thousands of years. Ancient civilizations, such as the Greeks and Romans, had their own explanations for this phenomenon. Over time, scientists like Isaac Newton contributed significantly to our understanding of the sequence of rainbow colors.
Newton's Contribution
Isaac Newton's experiments with prisms demonstrated that white light is composed of a spectrum of colors. His work laid the foundation for modern optics and helped explain why rainbows display their specific sequence of colors.
Cultural Significance of Rainbows
Rainbows hold deep cultural and symbolic meanings in many societies. In some cultures, they represent a bridge between the earthly and spiritual realms. Others see them as symbols of peace, diversity, and renewal.
Symbolism in Different Cultures
- In Norse mythology, the rainbow is the Bifröst, a bridge connecting Earth to Asgard.
- In Christianity, the rainbow is a sign of God's covenant with Noah.
- In modern times, the rainbow flag represents LGBTQ+ pride and unity.
Double Rainbows and Their Colors
A double rainbow occurs when light is reflected twice inside a water droplet, creating a second, fainter arc above the primary rainbow. The sequence of colors in a double rainbow is reversed, with red on the inner side and violet on the outer side.
How Are Double Rainbows Formed?
Double rainbows form under specific atmospheric conditions. The second reflection inside the droplet causes the colors to appear in reverse order, offering a unique and breathtaking sight.
Variations in Rainbow Colors
While the sequence of rainbow colors is consistent, variations can occur due to atmospheric conditions. Factors such as pollution, humidity, and the angle of sunlight can influence the appearance of a rainbow.
Factors Affecting Rainbow Colors
- Pollution can dim the colors of a rainbow.
- High humidity enhances the vibrancy of the colors.
- The angle of sunlight affects the visibility of certain colors.
Myths and Legends About Rainbows
Throughout history, rainbows have inspired countless myths and legends. These stories often reflect the cultural values and beliefs of the societies that created them.
Popular Rainbow Myths
- In Irish folklore, leprechauns hide their pots of gold at the end of a rainbow.
- In Native American traditions, rainbows are seen as a symbol of renewal and transformation.
- In Hindu mythology, the rainbow is associated with Indra, the god of thunder and rain.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes the Sequence of Rainbow Colors?
The sequence of rainbow colors is caused by the refraction, reflection, and dispersion of light within water droplets. Each color corresponds to a specific wavelength, resulting in the familiar order of red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet.
Can You Touch a Rainbow?
No, you cannot touch a rainbow. Rainbows are optical phenomena that depend on the position of the observer and the angle of sunlight. They do not exist as physical objects.
Why Are There Seven Colors in a Rainbow?
The seven colors of a rainbow correspond to the visible spectrum of light. Isaac Newton identified these colors based on his experiments with prisms, although some people argue that indigo and violet are too similar to be considered distinct.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The sequence of rainbow colors is a testament to the beauty and complexity of nature. From the physics of light refraction to the cultural significance of rainbows, this phenomenon continues to captivate and inspire people around the world. By understanding the science behind rainbows, we can appreciate their beauty even more.
We encourage you to share this article with others who might find it interesting. If you have any questions or comments, please leave them below. For more fascinating insights into the natural world, explore our other articles on this site.
References:
- National Geographic - https://www.nationalgeographic.com/
- Encyclopedia Britannica - https://www.britannica.com/
- NASA Science - https://science.nasa.gov/